Dislodged Gastrostomy Tube (G-Tube): How to Care for Your Child
Even with all of the right care, a gastrostomy (G-tube) sometimes gets dislodged (comes out of place).
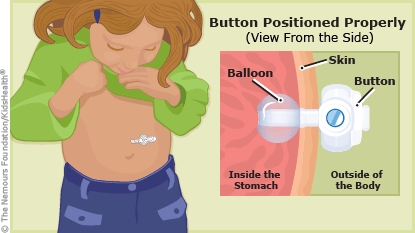

If the G-tube (either a long tube or flat "button") falls out of place, the hole can begin to close. The G-tube needs to be put back quickly (within 4 hours).
Children can dislodge a G-tube by pulling on it or by rolling over during sleep or getting it caught in something. The healing skin around the stoma, or opening, can push the G-tube out of place. The health care provider may prescribe creams or ointments to help the skin heal.
Your child's G-tube has been replaced and has been checked by the health care provider. Sometimes the health care provider may order a test to look for correct placement. It is now functioning normally.

-
Watch for signs of leakage onto the skin around the stoma.
-
Wash your hands before touching the G-tube.
-
Keep the area around the stoma clean and dry.
-
Put mittens on your child's hands before bed to keep your child from pulling on the tube while sleeping.
-
Apply prescription creams or ointments as directed.
-
If the health care provider prescribed antibiotics, make sure your child takes the entire course of medication as directed.


Your child:
-
Has leaking of fluid on the skin around the stoma.
-
Has soft, moist, pink-red tissue (called granulation tissue) coming out from around the G-tube.
-
Begins bleeding at the tube site.
-
Has a fever or signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or foul-smelling discharge.
-
Develops diarrhea.
Your child: