Birth Control: The Pill
The birth control pill ("the Pill") contains hormones that prevent pregnancy. The Pill is a reliable form of birth control.

-
It's important to use a condom every time you have sex (vaginal, oral, or anal), even when you're on the Pill, because:
-
Depending on where you were in your period cycle when you start the Pill, it might not work as birth control right away.
-
Condoms protect you from sexually transmitted diseases (STDs, also called STIs or sexually transmitted infections).
-
Using condoms while on the Pill makes it even less likely that you will get pregnant.
-
Start taking the Pill on the day recommended by your health care provider.
-
Take the Pill around the same time each day. Having a routine can help you remember — like taking it right after brushing your teeth in the morning or evening. You also can set up a daily reminder on your smartphone.
-
Check with your health care provider right away if you skip any pills. You may need to use another method of birth control.
-
Check with your health care provider if you get sick for more than 2 days with vomiting and diarrhea. This can make the Pill not work.
-
Don't smoke. Smoking puts you at risk for serious side effects from the Pill and many other medical conditions. If you need help quitting, go to teen.smokefree.gov or call 800-QUIT-NOW (800-784-8669).

-
You skipped one or more pills.
-
Taking a pill every day isn't working for you.
-
You have cramping, spotting, or irregular bleeding that continues after 6 weeks on the Pill.
-
You have heavy bleeding (soaking through a pad or tampon every hour for more than 2 hours).
-
You feel that the birth control pill has affected your mood.
-
You have signs of an STD (such as belly pain, fever, abnormal discharge, pain when peeing or having sex, or genital warts or sores), or if you had sex without a condom and are worried you could have an STD.
-
You start any new medicines, including antibiotics and herbal or natural medicines. Some can make the Pill not work.
-
Your skin or eyes look yellow, which can be signs of liver problems (a very rare side effect of the Pill).
You have lower leg pain, chest pain, trouble breathing, weakness, tingling, trouble speaking, or vision problems. These can be signs of a blood clot, which is an extremely rare side effect that can happen from the hormones in the Pill.

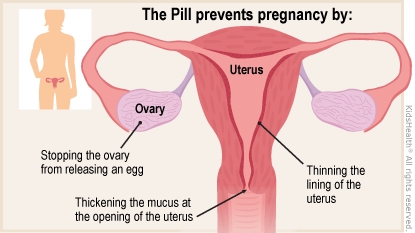
How does the Pill prevent pregnancy? The Pill:
-
prevents an egg from being released by the ovary
-
thickens the mucus at the opening of the uterus so that sperm can't get in
-
thins the lining of the uterus so that a fertilized egg can't attach to the wall of the uterus
What are the side effects from the Pill? The most common side effects are:
-
irregular or no periods
-
nausea, headaches, dizziness, or breast tenderness
-
mood changes such as nervousness or sadness
Some people worry the Pill will make them gain weight. But most people on the Pill stay at about the same weight. The Pill has some "good" side effects too — it can make periods lighter or more regular, make cramps less severe, ease PMS (premenstrual syndrome) symptoms, and improve acne.
What if I have sex before the Pill is working and I don't use a condom or it breaks? Emergency contraceptive ("morning after") pills are available at the pharmacy without a prescription or ID. They delay ovulation (the release of an egg). This way there is no egg for the sperm to fertilize. If the egg was already fertilized and implanted in the uterus wall, emergency contraceptive pills will not stop the pregnancy.