Mastoiditis: How to Care for Your Child
Mastoiditis occurs as a rare complication of an ear infection. It can be mild or severe, and early treatment can help prevent more serious problems.
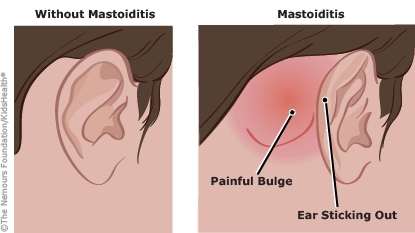

Mastoiditis is an infection of the mastoid, a bone right behind the ear that has air cells that connect, resembling a honeycomb. Mastoiditis can occur when an infection in the middle ear spreads into these air cells.
Mastoiditis can make the area behind the affected ear red, tender, and swollen. It can make the ear stick out more than usual from the head and cause fever and crankiness. Sometimes, fluid drains from the ear.
The health care provider may have used blood tests and/or X-rays to learn more about your child's infection.
Your child received antibiotic treatment in the hospital and may need to continue taking antibiotics at home. Surgery is sometimes needed to help drain the infection.

-
Give your child all of the antibiotics as directed, even if he or she is feeling better in a few days.
-
If your child has pain or is uncomfortable from a fever, a medication may help your child feel better:
-
For children under 6 months, you may give acetaminophen.
-
For children over 6 months, you may give acetaminophen OR ibuprofen, if recommended by your health care provider.
-
Allow your child to rest as needed.
-
If the infection was drained, follow the health care provider's instructions for care after the procedure.


-
Your child's symptoms get worse, do not improve, or return.
-
Your child develops new symptoms.
Your child:
-
Has any hearing problems.
-
Develops neck pain and/or stiffness, a severe headache, or a new fever.
-
Is unusually drowsy, has trouble moving or speaking, has a seizure, or loses consciousness.