Acute Glomerulonephritis
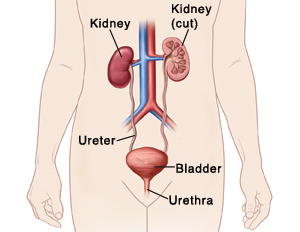
The kidneys remove waste products and extra fluid from the blood. Glomerulonephritis (GN) is an inflammation of the kidney. It affects how well the kidneys filter blood and get rid of wastes. You may also hear the terms nephritis and nephrotic syndrome used. This condition may last weeks to months (acute) or may last many years (chronic).
It can follow a bacterial or viral infection. These may include a strep infection of the throat or skin. An immune reaction or inflammation of the blood vessels in the kidney may also be the cause.
Symptoms of GN include:
-
Cola- or iced-tea-colored urine due to small amounts of blood in the urine
-
Swelling of the face, hands, feet, and abdomen (edema)
-
Tiredness
-
Making less urine than before
Treatment depends on the exact cause of GN. Most types of acute GN recover fully. In some cases, acute GN can become chronic. It can lead to problems requiring dialysis. It's important that your healthcare provider monitors you closely.
Home care
These guidelines will help you care for yourself at home:
-
If a bacterial infection is the cause of your acute GN, you will be given antibiotics. Take them all as directed. People who have had close contact with you should see their healthcare provider for testing and possible antibiotic treatment.
-
Short-term bed rest is advised until kidney function improves.
-
If you have signs of swelling, eat less salt. Your healthcare provider may suggest a strict kidney diet.
-
Don't take any of the following over-the-counter medicines, or talk with your provider before using:
-
Aspirin and anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen and naproxen. Short-term use of acetaminophen for fever or pain may be OK. But talk with your provider first.
-
Laxatives and antacids that contain magnesium or aluminum
-
Certain stomach acid-blocking medicine such as cimetidine or ranitidine
-
Herbal supplements
Follow-up care
Follow up with your provider, or as advised. The following resources may be helpful:
Call 911
Call 911 if you have any of these:
-
Severe weakness, dizziness, fainting, drowsiness, or confusion
-
Chest pain or shortness of breath
-
Fast, slow, or irregular heartbeat
When to get medical advice
Call your healthcare provider right away if any of these occur:
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Unexpected weight gain or swelling in the legs, ankles, or around the eyes
-
Decreased or absent urine output
-
New or worsening symptoms
Online Medical Reviewer:
Marianne Fraser MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Raymond Kent Turley BSN MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Walead Latif MD
Date Last Reviewed:
9/1/2022
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.